Table of Contents
After Bitcoin, Ethereum is the cryptocurrency system that is incredibly popular amongst investors and developers. Launched in 2015, it has positioned itself as the world’s first programmable blockchain.
According to ConsenSys, Ethereum is a ‘world computer’. What that means is that the second most valuable blockchain is open for anyone to create applications. But why?
Because the existing global software development infrastructure is based on a centralized client-server model.
Ethereum wants to replace that model, decentralize software development, and eliminate central points of failure/control. Piqued?
If yes, then let’s go deeper!
Brief History
As a 17-year old programmer, Ethereum creator and lead developer, Vitalik Buterin started tinkering with Bitcoin in 2013. The limitless possibilities of blockchain, Bitcoin‘s underlying mechanism enthralled him.
Get WazirX News First
Consequently, he attempted to develop applications on top of Bitcoin through the Mastercoin project. Buterin envisioned a platform that is robust enough to develop ‘decentralized applications’ after facing several roadblocks.
Along with the platform, Vitalik also thought of writing an entirely new programming language that application creators could use globally to develop applications on Ethereum.
Finally, in November 2013, he presented the Ethereum whitepaper. Subsequently, his decentralized computing idea began garnering significant interest and attention.
In 2014, Buterin and the other co-founders Joseph Lubin, Anthony Di Iorio, and Charles Hoskinson kickstarted the Ethereum token sale. The crowdfunding campaign went on from July to September that year and raised more than $15 million for the project.
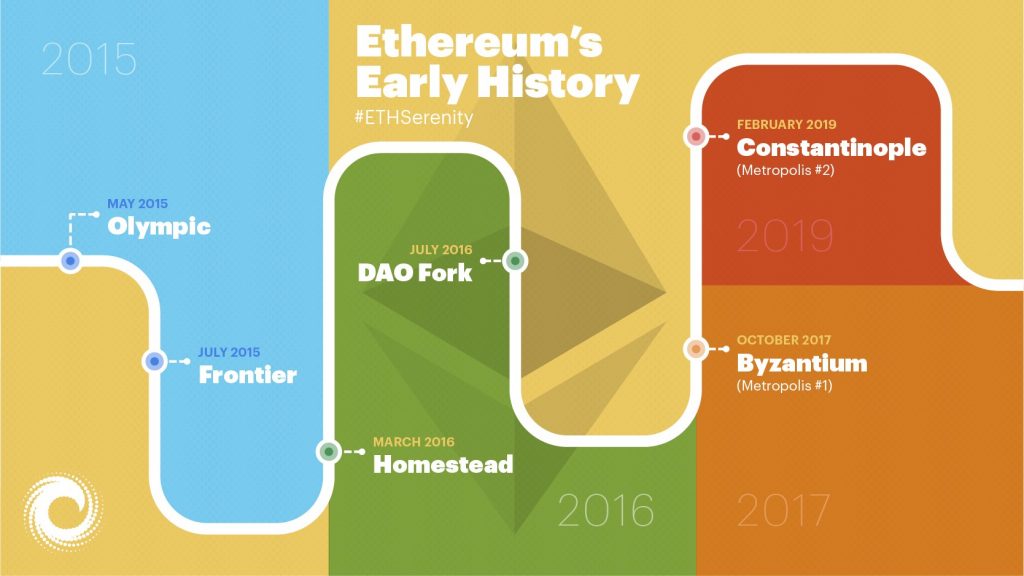
As per official records, exactly, one year after the launch of the crowd sale, the Ethereum blockchain went live in July 2015.
Mainnet Launch and Upgrades
Frontier (a.k.a Frontier ‘mainnet’) Ethereum’s first version went public in July 2015. Mainnet is a term that folks in the cryptocurrency community use for blockchain protocols that are fully developed.
But before the Frontier mainnet went live, developers released the Olympic ‘testnet’ to test all aspects of Frontier before releasing it to the world.
Like mainnet, a testnet is a ‘test blockchain’ that programmers use to troubleshoot and sanitize the mainnet for errors and code loopholes.
With the launch of Frontier, developers could finally start building applications on Ethereum, and miners could start mining Ether (ETH), Ethereum’s native cryptocurrency.
Frontier was followed by the Homestead upgrade. Since the beginning, upgrades on Ethereum have been carried out through ‘hard forks’. Check out the video below to know more about them.
Homestead introduced Ethereum Improvement Protocols or EIPs to spruce up the Ethereum blockchain. Actioning EIPs bumped up quite a few features paving the way for future updates.
The core development team planned all upgrades and hard forks except 2016’s DAO fork. While all hard forks have led to upgrades, the DAO hard fork led to the creation of a new cryptocurrency – Ethereum Classic. See the video below to know more.
Ethereum continued improving further after the DAO drama with the Byzantium (October 16, 2017) and the Constantinople (February 28, 2019) upgrades.
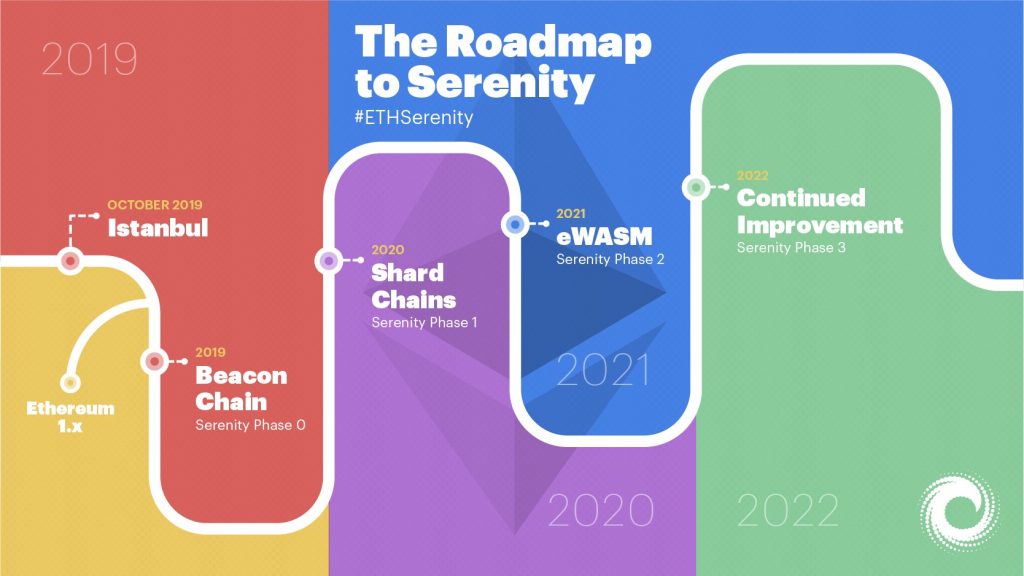
The blockchain platform will continue to improve its architecture through Istanbul and Serenity hard forks. Also, with Serenity, Ethereum plans to move from a Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus protocol to Proof-of-Stake (PoS).
How Does Ethereum Work?
Before delving deeper into Ethereum’s working, it makes sense to know a few basic things:
- Smart contracts – Programs or code designed to execute upon fulfillment of certain pre-defined conditions. Solidity, Ethereum’s native programming language for developing smart contracts. This video will illustrate it better:
- Decentralized Applications (dApps) – Decentralized applications are the reason that started everything. They can be anything – websites, programs/software that run on Ethereum. dApps operate through smart contracts.
To look at it simply, the Ethereum system comprises of three layers. The first layer is the public ledger or blockchain. Second is the ‘smart contracts layer’ where developers use Solidity to write code for dApps. This layer also executes the designed dApps.
And the last layer is the ‘dApps layer’ where decentralized applications interact with users.

How Ethereum Found it’s Use Case with DeFi
Bitcoin promised to decentralize payments, monetary supply, and issuance. But there was a need to democratize access to broader financial instruments like lending, borrowing, investing (for interest-based returns).
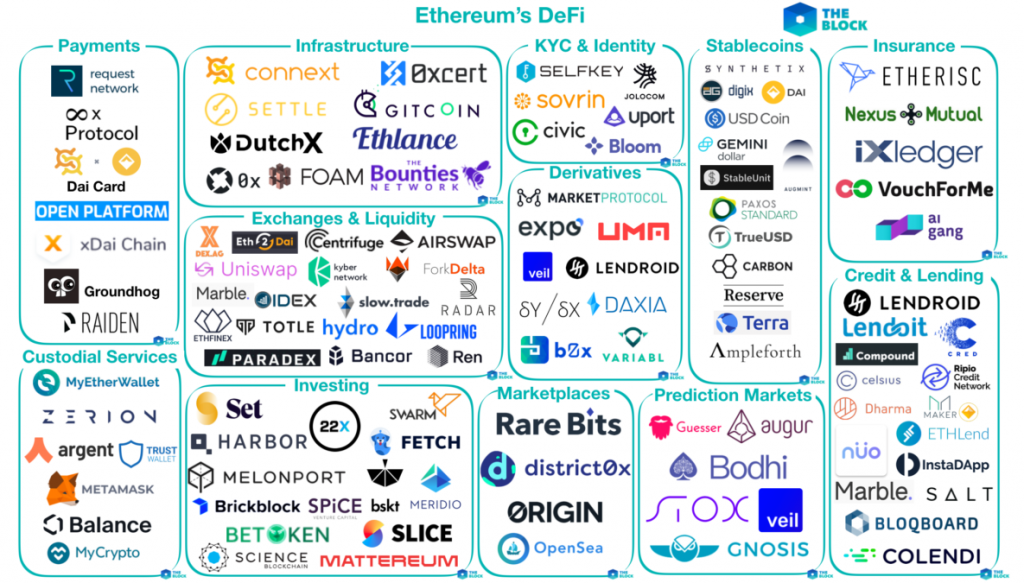
That’s how ‘decentralized finance’ or DeFi came into being. All DeFi protocols are based on Ethereum and have the following features:
- Interoperable
- Programmable – smart contracts drive decision making in the DeFi ecosystem, not humans
- Composable – the entire system is like a box of Lego blocks — there is absolutely no limit to what can be built
The map below best represents the DeFi ecosystem
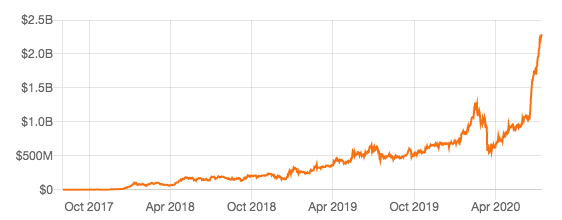
DeFi is an increasingly burgeoning space, with the total value recently crossing the $2 billion mark.
Compound is the most valuable token in the DeFi market and is now available for trading on WazirX.
What is Ether (ETH)? How and Where to buy it?
Ether or ETH is Ethereum’s native cryptocurrency. It powers all financial transactions on the second largest blockchain.
Apart from monetary transfers, ETH finds use in all interactions involving smart contracts and dApps.
As opposed to bitcoin’s maximum supply of 21 million BTC, ETH doesn’t have a cap on its supply. The total number of ETH in circulation surpassed the 100 million mark couple of years ago. The current circulating supply stands at over 111 million.
ETH is a pretty popular crypto asset amongst investors and has returned immense profits since it first started trading. At WazirX, we provide you a smooth and seamless way to buy ETH. To know more about using the WazirX mobile app, check out the video below:
Further Reading:
What are the Differences Between Bitcoin and Ethereum?
What are the Differences Between Ripple (XRP) and Ethereum (ETH)?
What is the difference between Litecoin and Ethereum?
What is Ethereum 2.0? Is it different from Ethereum?
5 Reasons Ethereum Momentum is Accelerating
ETH 2.0 Beacon progress, what to expect next?
Ethereum price prediction: Will it hit $5000 in 2021?
5 Things to Keep in Mind While Buying or Selling Ethereum
What is the difference between Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Ripple?
Also you can download the app and Start Trading Now!
Android App – WazirX – Buy Bitcoin & Cryptocurrency Exchange
iOS App – WazirX
 Disclaimer: Click Here to read the Disclaimer.
Disclaimer: Click Here to read the Disclaimer.






















2 Comments